Data has never been so needed and openly accessible as it is today. Why?
This is because Accurate and up-to-date information drives modern technology, businesses, major decisions, strategic approaches to problems, access to resources around you e.t.c
The need to harvest such data, openly available on the web in an automated fashion, prompts web scraping techniques.
What is web scraping?
In simple terms it's a technique employed to extract specific amounts of data from websites whereby the data is extracted and saved to a local file in a computer or to a database. So instead of manually copying the data from websites, the Web Scraping tool will perform the same task within a fraction of the time.
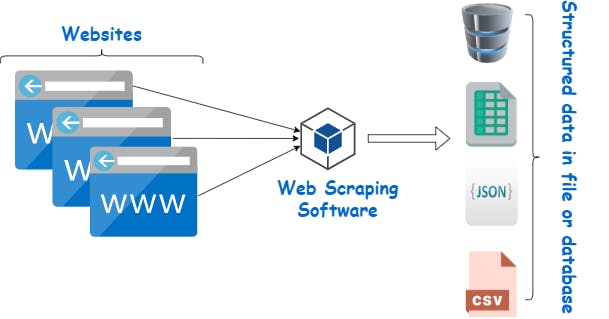 Photo by WebHarvy
Photo by WebHarvy
Let's demo a simple data harvest in Nodejs, Tools needed:
- Puppeteer - it's a Node library which provides a high-level API to control Chrome. its also a headless browser and a pretty fast tool.
- Nodejs - Node.js® is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine, for server side applications.
Getting started
Installation.
To use Puppeteer in your project, run:
npm i puppeteer
# or "yarn add puppeteer"
Nodejs server setup.
Let's spin up a Nodejs sever to respond to our web scraper API call,
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const cors = require('cors')
const dotenv = require('dotenv');
dotenv.config()
// scraper model class
const Scrapers = require('./Scrapers');
app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
app.use(cors())
// api routes
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('welcome!')
})
// web scraper API route
// it accepts just the websiteURL as parameter
app.post('/api/v1/scrape', (req, res) => {
let productUrl = req.body.url
let scraper = new Scrapers()
scraper.scrapeAmazonStore(productUrl)
.then(data => {
res.status(200).json({
status: true,
message:data
})
})
.catch(err => {
res.status(400).json({
status: false,
message: err
})
})
})
// catch 404 and forward to error handler
app.use((req, res, next) => {
next(res.status(400).json({
status: false,
data: 'Bad request'
}));
});
// error handler
app.use((err, req, res) => {
// render the error page
res.status(err.status || 500).json({
status: false,
data: 'internal server error'
});
});
app.listen( process.env.PORT, () =>
console.log(` listening at http://localhost:${process.env.PORT}`)
)
Usage.
For this use-case, this API needs to be very simple and we intend to target one website and scrape specific data.
Amazon store is a great place to start 😀 and get the data of a product's price, title and landing-image .
Now let's get what we need
- Product url
- And the location of the specific information on the website
Implementation.
- The scrapeAmazonStore method takes the product's url, let's get it
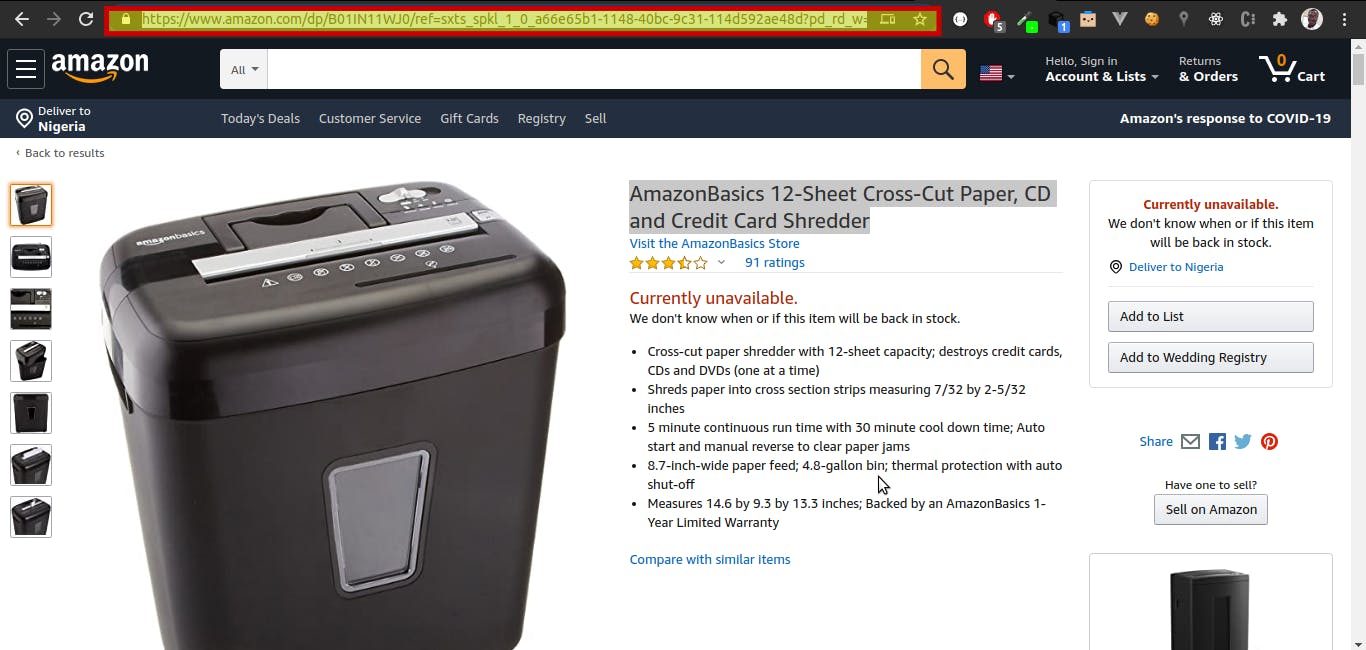
- To get specific data of the web page, we need to target its HTML, We achieve this by, inspecting the content we need > and copy the xpath of the HTML
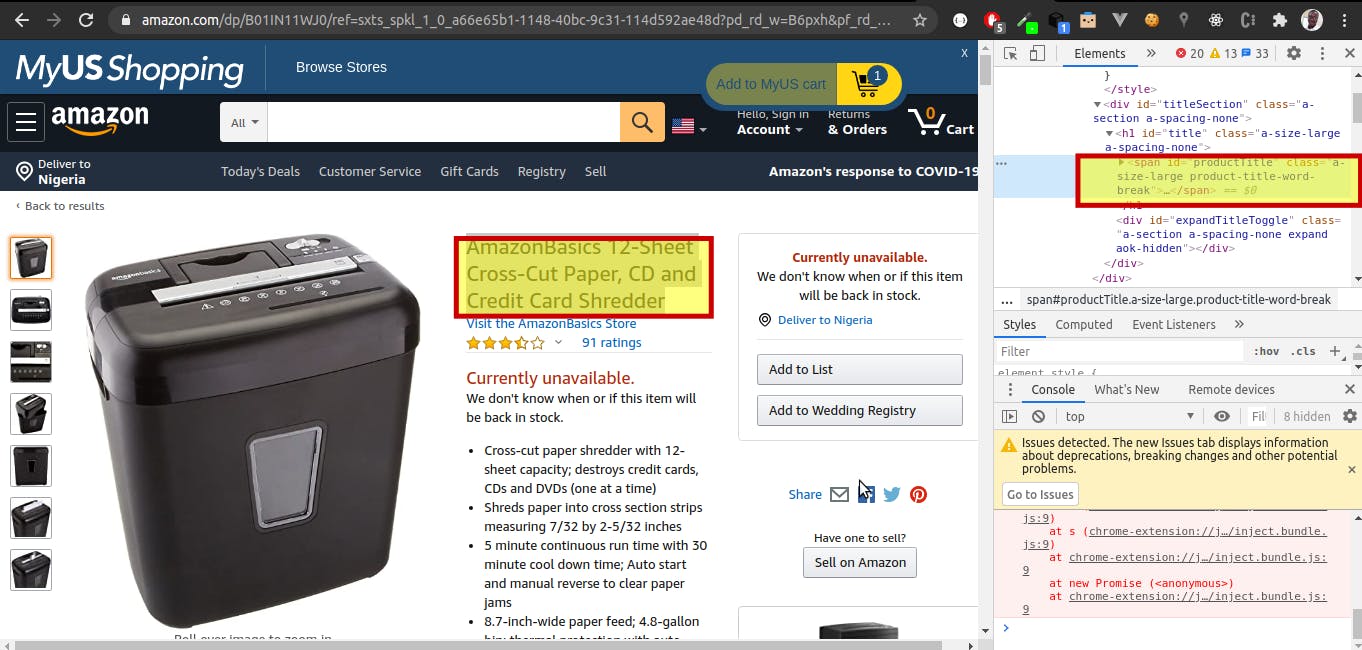
Let's write the model ScrapeProduct class:
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
class ScrapeProduct{
async scrapeAmazonStore(url){
try {
// we stated ealier that puppeteer library is headless browser, i.e no browser-GUI
// we start off by launching the browser asychronously
const browser = await puppeteer.launch({
headless:true,
args: [
'--no-sandbox'
],
});
// open a new web page
const page = await browser.newPage();
// goto the product url that was parsed
await page.goto(url);
//get product imgUrl
// insert the product image xpath
// web crawlers understand xpath
const [el] = await page.$x('//*[@id="landingImage"]');
const src = await el.getProperty('src');
const imgUrl = await src.jsonValue();
// get product title
// insert the product title xpath
const [el2] = await page.$x('//*[@id="productTitle"]');
const txt = await el2.getProperty('textContent');
let title = await txt.jsonValue();
// get product price
// insert the product price xpath
const [el3] = await page.$x('//*[@id="priceblock_ourprice"]');
const txt2 = await el3.getProperty('textContent');
const price = await txt2.jsonValue();
// return an object containing the product's image, title and price
return{
imgUrl,
title,
price
}
// close the headless browser
browser.close()
} catch (error) {
console.log(error)
return error
}
}
}
module.exports = ScrapeProduct
All set and configured , let's test the API 😇:
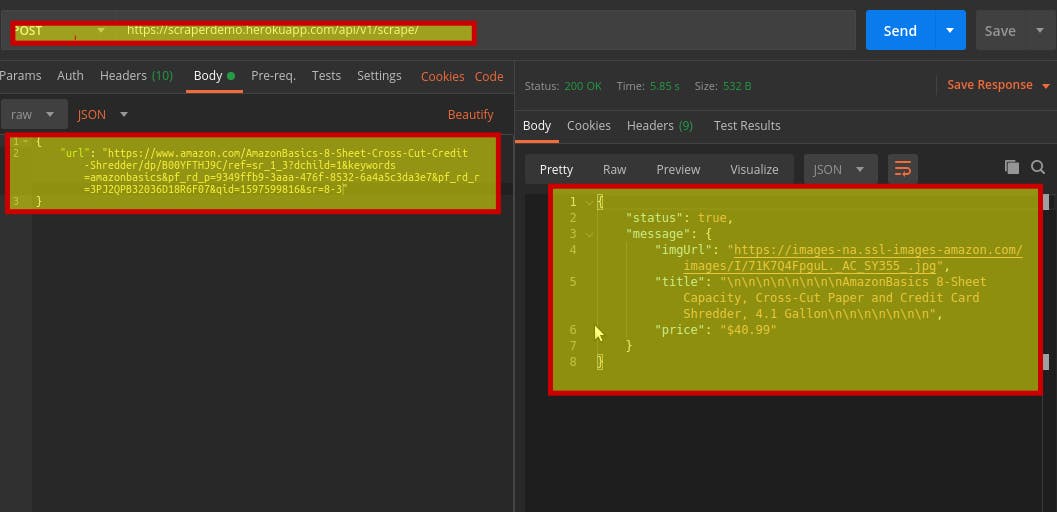 The API successful returns data about the product 😎 ! well this API could be better, in terms of its
The API successful returns data about the product 😎 ! well this API could be better, in terms of its
- Response time
- Robustness to support multiple stores
- Generic to support all kinds of products etc
Feel free to use the scraperdemo API as a template to build your ideas 👍 and do drop a star ⭐ on the scraperdemo project.
Thanks for the audience 🤗 and connect with me on Github, linkedIn and Twitter.
