Photo by Nicolas Hoizey on Unsplash
CloudWatch Events vs. EventBridge: Which is Best for Your AWS Glue Jobs and Step Functions?
🌩️ Cloud computing has revolutionized how applications are developed and deployed, providing a more flexible and scalable environment for running workloads. AWS offers several services for event-driven computing, including Amazon CloudWatch Events and Amazon EventBridge. This article will explore the differences between CloudWatch Events and EventBridge and discuss which is best for your AWS Glue Jobs and Step Functions.
🎯 This article targets developers, architects, and AWS users who want to better understand the differences between CloudWatch Events and EventBridge and choose the most suitable service for triggering AWS Glue Jobs and Step Functions workflows.
🌟 Understanding Event-Driven Computing on AWS
According to the AWS documentation, event-driven computing is a computing model in which an application responds to events, which can be generated either by a user, a software system, or a hardware device. AWS offers several services for event-driven computing, including Amazon CloudWatch Events and Amazon EventBridge.
💻 CloudWatch Events vs. EventBridge: Key Differences
When choosing between CloudWatch Events and EventBridge, it is essential to understand their differences.
👴 Maturity: CloudWatch Events is an older service compared to EventBridge. Suppose you already use CloudWatch Events in your environment and only need basic event routing and triggering for Glue Jobs and Step Functions. In that case, it might make sense to continue using CloudWatch Events.
🔌 Flexibility and Integration: EventBridge offers more flexibility and integration capabilities, especially when working with custom events or third-party SaaS providers. If your Glue Jobs or Step Functions workflows require complex event filtering, transformation, or integration with external services, EventBridge is a better choice.
🚌 Event Bus and Event Routing: EventBridge uses an event bus to manage and route events, providing better control and visibility over event routing and delivery. This feature can be beneficial when coordinating multiple event sources and targets or needing more granular control over event processing.

🚀 Scalability: EventBridge is designed to handle large volumes of events and offers better scaling capabilities than CloudWatch Events. If you anticipate high event throughput for your Glue Jobs or Step Functions workflows, consider using EventBridge.
🌩️ Using CloudWatch Events with AWS Glue Jobs
AWS Glue is a fully-managed extract, transform, and load (ETL) service that enables you to move data between data stores. In addition, you can use CloudWatch Events to trigger Glue jobs when specific events occur in your AWS environment.
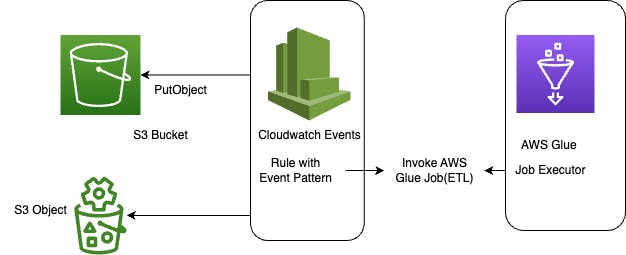
👉 Here's an example of how you can use a CloudWatch Events rule to trigger a Glue job when a new object is created in an S3 bucket:
{
"source":[
"aws.s3"
],
"detail-type":[
"AWS API Call via CloudTrail"
],
"detail":{
"eventName":[
"PutObject"
],
"requestParameters":{
"bucketName":[
"my-bucket"
]
}
}
}
🌩️ Using EventBridge with AWS Step Functions
AWS Step Functions is a fully-managed service that enables you to coordinate multiple AWS services into serverless workflows. You can use EventBridge to trigger Step Functions workflows when specific events occur in your AWS environment.
👉 Here's an example of how you can use an EventBridge rule to trigger a Step Functions workflow when an EC2 instance is stopped:
{
"source":"aws.ec2",
"detail-type":"EC2 Instance State-change Notification",
"detail":{
"state":"stopped"
}
}
🔍 Prerequisites and Best Practices
Before using CloudWatch Events or EventBridge with Glue jobs or Step Functions, consider the following prerequisites and best practices:
✅ Ensure that your AWS environment is configured correctly and you have the necessary permissions to create and manage CloudWatch Events or EventBridge rules and targets.
🎯 Define explicit event schemas and rules that match your specific use cases and requirements.
🔎 Use filtering and transformation capabilities to limit the number of events processed and to optimize the event payload for downstream services.
🧪 Test and validate your event-driven workflows to ensure that they are working as expected, and use monitoring tools like CloudWatch to monitor the performance and health of your workflows.
In conclusion, choosing between CloudWatch Events and EventBridge depends on the specific requirements of your application. For example, if you only need basic event triggering and routing, CloudWatch Events might be sufficient. However, if you require more advanced event processing, integration, and scalability, EventBridge is better for managing your AWS Glue Jobs and Step Functions workflows.
Remember to follow best practices and optimize your event-driven workflows for performance and scalability. By choosing exemplary event-driven service and best practices, you can build scalable and resilient applications on AWS.
If you have any inquiries or wish to gain additional knowledge, please get in touch with me on GitHub, Twitter, and LinkedIn. Moreover, kindly show your support by leaving a thumbs up 👍, a comment 💬, and sharing this article with your network 😊.
References:
AWS Documentation, Amazon EventBridge. aws.amazon.com/eventbridge
AWS Documentation, What is AWS Glue? aws.amazon.com/glue
AWS Documentation, What is AWS Step Functions? aws.amazon.com/step-functions

